
It might be uncomfortable to experience stomachaches, indigestion, heartburn, and other digestive problems. Some gastrointestinal symptoms go away by themselves. However, other signs and symptoms, particularly if they are persistent, may point to a digestive issue.

Discover a list of the top 10 digestive diseases by reading this article. The causes, prevalence, and an outline of each condition’s therapies are all included in the brief descriptions. Who to call for stomach issues is also covered on this page.
Discover a list of the top 10 digestive diseases by reading this article. The causes, prevalence, and an outline of each condition’s therapies are all included in the brief descriptions. Who to call for stomach issues is also covered on this page.
What exactly are stomach issues?
The gallbladder, liver, pancreas, and other digestive system organs are among those that are impacted by digestive illnesses.
The digestive system is in charge of breaking down food and liquids so that your body can absorb the nutrients. These nutrients are utilized by the body for energy, cell development, and repair. Wastes are also eliminated through the digestive system.
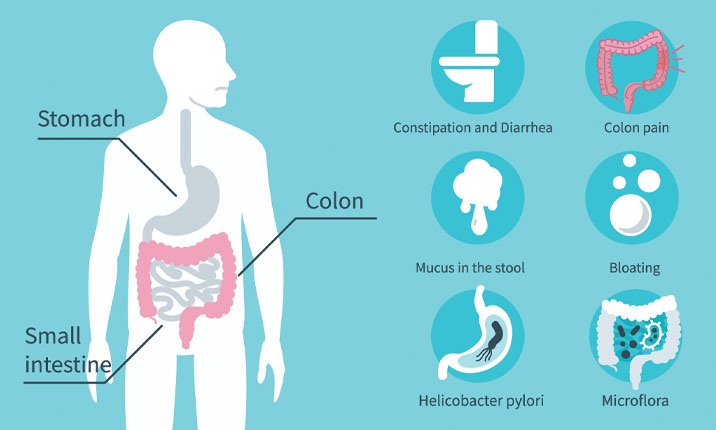
With at-home care, some intestinal problems get better on their own. However, it could be necessary to see your doctor if your gastric problem symptoms worsen or continue to persist.
Continue reading for a summary of 10 common digestive problems, along with information on their signs, causes, the propensity in the US, and treatments.
1. Gastrointestinal reflux disease
You may have gastroesophageal reflux disease if you have heartburn or acid reflux more frequently than a few times per week (GERD).
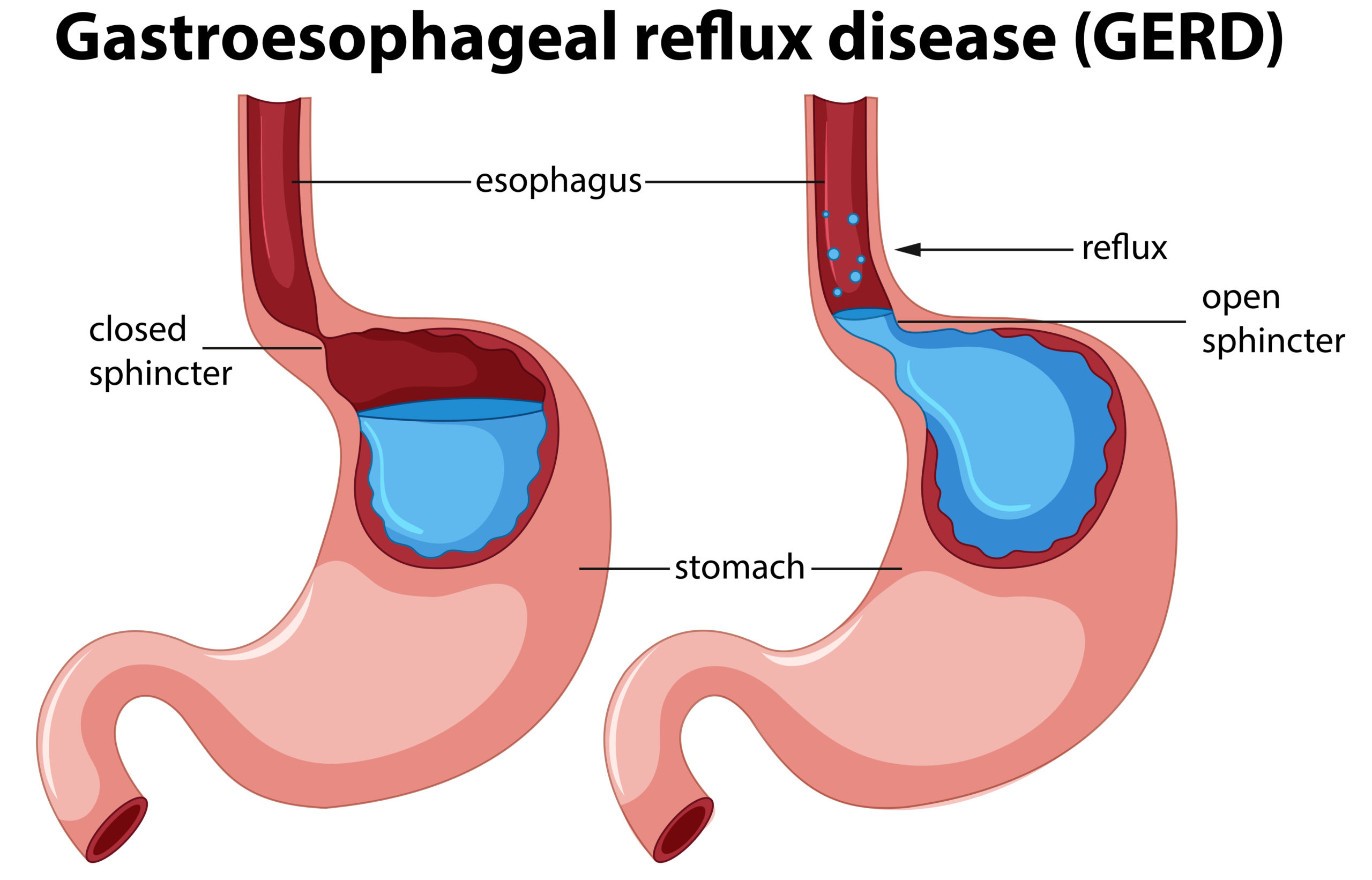
What causes GERD?
The esophagus transports food you’ve swallowed down to your stomach. The lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscles, links the stomach and esophagus.
Stomach acid might leak back up into your esophagus if the LES isn’t functioning properly. It gives you heartburn. Your esophagus may suffer substantial harm as a result over time.
How common is GERD?
Approximately 20 percent of Americans suffer from GERD.
How is GERD managed?
By altering your food and lifestyle, you can treat GERD. They consist of the following:
Consume smaller meals.
After eating, do not lie down for two hours. Additionally, avoid eating within two hours of going to bed.
Refrain from consuming coffee, spicy meals, fats, citrus, and other high-acid foods and liquids.
Use an under-mattress foam wedge to raise the head of your bed by 6–8 inches.
Consult your doctor before taking antacids or acid blockers with a prescription.
2. Gastritis and peptic ulcer disease
An open sore on the stomach or upper small intestine lining is referred to as peptic ulcer disease (PUD). It is uncommon for a peptic ulcer to form in the esophagus right above the stomach.
Gastritis is the medical term for stomach lining inflammation.
Both of these disorders share comparable origins and symptoms, such as nausea and stomach pain.
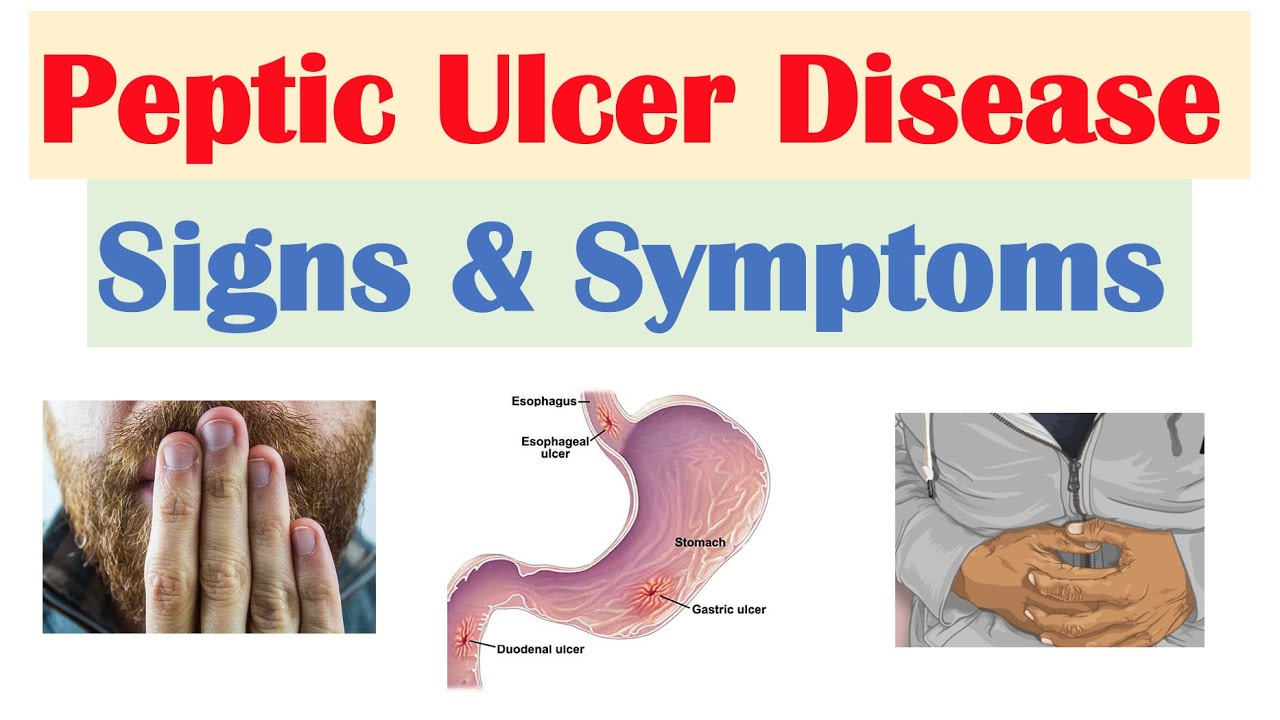
Why do PUD and gastritis occur?
The most typical cause of PUD is a bacterial infection called Helicobacter pylori, which frequently results in chronic gastritis. Another typical cause is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), which include aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen.
How common are gastritis and PUD?
In the US, PUD affects close to 15 million adults. This equates to around 6% of the adult population.
How are PUD and gastritis treated?
A majority of ulcers will heal with treatment. PUD therapies include the following:
Stomach acid can be decreased using antacids and proton pump inhibitors.
- pylori infections can be treated with antibiotics.
The ulcer may be covered with protective drugs, allowing it to recover.
Treatment options for a bleeding ulcer during an esophagogastroduodenoscopy operation include medicines, a clamp, or cauterization
3. Stomach flu
Viral gastroenteritis, sometimes known as stomach flu, is an infection of the intestines. Vomiting, cramps, stomach pain, and diarrhea are a few typical symptoms.
Although it is frequently used, the term “stomach flu” is not accurate in medicine. The “flu” virus does not cause it, and the infection targets the intestines rather than the stomach.

What causes stomach flu?
The cause is frequently a virus, like rotavirus or a norovirus.
How common is the stomach flu?
The most typical cause of stomach flu is norovirus. Each year, it contributes to 19–21 million cases of viral gastroenteritis in the US.
How is stomach flu treated?
The majority of the time, gastroenteritis goes away on its own, although vomiting and diarrhea cause you to lose fluids. By consuming electrolyte drinks and water, you can avoid being dehydrated.
4. Gluten intolerance and celiac disease
Celiac illness and gluten sensitivity have many of the same symptoms. They include bloating, stomach pain, and diarrhea. It’s crucial to speak with your doctor to get the right diagnosis.

What causes celiac disease and gluten sensitivity?
Celiac disease, in contrast to gluten sensitivity, is an autoimmune disorder that can harm the small intestine. Malnutrition may result from this damage’s impact on vitamin and mineral absorption.
How common are celiac disease and gluten sensitivity?
About 6% of people have gluten sensitivity that is not caused by celiac disease. The prevalence of the true celiac disease is less than 1%.
How are celiac disease and gluten sensitivity managed?
The basic course of treatment for both ailments is to cut out gluten from your diet, which is a protein found in wheat, rye, barley, and oats.
If you are told you have celiac disease, your doctor will probably examine your vitamin and mineral levels and, if necessary, prescribe supplements.
5. Inflammatory bowel disease
Chronic digestive tract inflammation is known as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The two most prevalent IBDs are ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease.
IBD produces inflammation and irritation, which frequently leads to diarrhea, stomach pain, loss of appetite, fever, and weight loss.
The beginning of the colon and the end of the small intestine are primarily affected by Crohn’s disease. Colon and rectum tissue are impacted by ulcerative colitis.
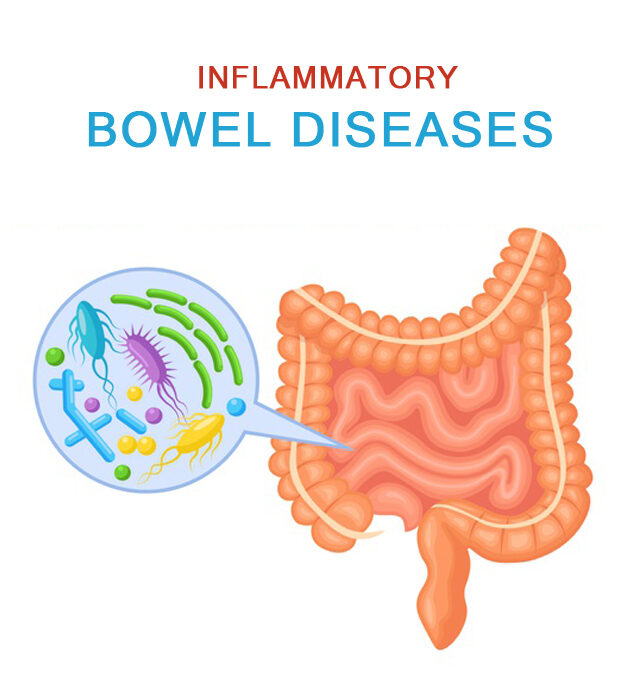
What causes IBD?
These autoimmune diseases, which eventually result in IBD, are brought on by an unexpected immune response. IBD’s precise causes are unclear. The inflammation may start as a result of a viral, bacterial, or allergic reaction.
How common is IBD?
About 3 million Americans have IBD, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
How is IBD managed?
The disorder that underlies IBD will determine how it is treated. Medication is frequently used in treatment to:
Suppress your immune system
Lessen inflammatory
Infection control or prevention
A severe case of diarrhea
Avoid using NSAIDs to treat minor discomfort
Surgery may occasionally be required to manage issues like intestinal blockages or abscesses.
If you frequently get diarrhea or if you have lactose intolerance, your doctor may advise a low-fiber diet.
6. Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and IBD are occasionally confused by people. IBS is a collection of symptoms that happen at least three times each month for three consecutive months, including changes in bowel habits and abdominal pain. Bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and mucus in the stool are examples of symptoms.
IBS does not affect the digestive tract, in contrast to IBD. IBS is also much more prevalent.

What brings on IBS?
IBS’s precise cause is unknown. Although they seem to have an impact, several factors appear to have varying effects on people with IBS. These consist of:
Stress
Gastrointestinal bacterial infections
Mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety
Food intolerances or sensitivities
How common is IBS?
IBS is present in about 12% of Americans.
How is IBS managed?
Treatment options include:
Consuming more fiber, consuming smaller meals, and eating a low-FODMAP diet.
Avoiding symptoms-causing foods
Getting enough sleep and engaging in regular physical activity
Lowering anxiety
To treat IBS, some people use laxatives, fiber supplements, or probiotics. Keeping a food journal can help you find the foods and situations that make your symptoms worse.
For the treatment of abdominal pain, doctors may recommend medicines. Therapies for mental health conditions may also help reduce IBS symptoms.
7. Constipation
Constipation is the inability or irregularity of passing stools. You probably have constipation if you only go to the bathroom three times per week or less. Constipation is characterized by difficult bowel movements and firm stools.

What brings about constipation?
Constipation can be brought on by dehydration, a diet low in fiber, some drugs, and medical conditions that delay the digestive process.
How frequent are constipations?
In the United States, 63 million people struggle with chronic constipation.
How is constipation handled?
Increasing fiber, hydration intake, and exercise will typically cure this disease. Stool softeners and laxatives should only be used as a last resort. Avoid depending on these solutions for an extended period of time.
8. Hemorrhoids
In the anal canal, hemorrhoids are painful, bulging blood vessels. Pain, itchiness, and bright red blood following a bowel movement are symptoms.

Why do hemorrhoids develop?
Pregnancy and chronic constipation are the main contributors. Other potential causes include experiencing persistent diarrhea, straining to go to the bathroom, and spending a lot of time on the toilet.
Hemorrhoids: How common are they?
In the United States, around 1 in 20 persons suffer from hemorrhoids. They are present in half of the people over 50.
How are hemorrhoids managed?
Constipation can be avoided by increasing your intake of fiber and water. To ease pain and itching, try hemorrhoid treatments, suppositories, or a warm bath.
Even though it could be embarrassing to discuss hemorrhoids, try not to let that deter you from getting help if they don’t go away.
9 Diverticular disease
Diverticular disease includes diverticulitis, which is the inflammation of the colon’s wall, and diverticulosis (when these pouches become inflamed). You can feel bloated, have loose stools, or have lower abdominal pain.

What causes diverticular disease?
Diverticular illness has an unknown cause. Genes might be involved. Additional elements that could raise the likelihood of contracting the illness include:
Eating a diet high in red meat and low in fiber
Getting very little to no exercise
NSAID and steroid use
Having an immune system-related ailment
How common is diverticular illness?
Diverticulosis affects more than 30% of Americans aged 50 to 59 in the country. More than 70% of people over the age of 80 have it. Less than 5% of persons with diverticulosis go on to develop diverticulitis.
Some individuals never experience symptoms.
How is diverticular illness managed?
Changing your diet is a common component of treatment.
Do not delay calling your doctor if you are experiencing rectal bleeding. To cure diverticulitis, you might require antibiotics, a liquid diet, or surgery.
10. Gallstones
The digestive juice bile is kept in the gallbladder. In order to aid in food digestion, it also releases bile into your small intestine. Gallstones are tiny, hard deposits that can develop from this bile. The medical name for gallstones is cholelithiasis.
Some gallstones disappear on their own and do not produce any symptoms. Others may result in infection or excruciating discomfort. Along with fever, nausea, and vomiting are possible.

What causes gallstones?
Gallstones can develop when the bile contains excessive quantities of bilirubin or cholesterol. Additionally, rapid weight reduction can make gallstones more likely to form. Overweightness is another risk factor.
The frequency of gallstones
Gallstones affect about 25 million Americans, however, not all of these instances are serious.
How are gallstones handled?
Gallstones that cause assaults on the gallbladder are typically treated surgically. Other gallstones can be broken up or removed using nonsurgical methods.
Who to call if you have intestinal issues
Your primary care physician can be the first place you go if you are having problems with your digestive system.
Most digestive problems can typically be treated first by primary care physicians.
Your primary care physician might later suggest that you see a gastroenterologist in particular circumstances. A gastroenterologist, often known as a gastrointestinal physician, is an expert in identifying and treating digestive system disorders.
Summary
Any organ in the digestive system may be affected by digestive diseases. The condition, the organ it affects, and the cause all have a significant impact on the symptoms. With home care, some stomach issues get better on their own.
However, sometimes gut issues can be a sign of a more serious medical issue. It could be necessary to call your doctor if your symptoms continue or suddenly get worse.







